At the interface
Sphingolipids, or SLs, have emerged as critical players in membrane stability and as essential signaling molecules. SLs range from abundant species involved in maintaining membrane integrity, such as sphingomyelin, to scarce and potent signaling species, such as sphingosine-1-phosphate, or S1P. S1P mediates critical signaling functions through interaction with its cognate G-protein coupled receptors in development and in several disease states. In recent decades, many resources have been devoted to understanding how S1P generation is regulated.
S1P can be generated through the action of two sphingosine kinase isoforms. The more commonly expressed of the two is sphingosine kinase 1, or SK1. This enzyme has garnered attention as a potential therapeutic target, as it often is upregulated . To gain access to its substrate, sphingosine, and to release its product, S1P, SK1 must interact directly with membranes. However, how SK1 achieves membrane binding has been contested in the literature. How does a cytosolic lipid-metabolizing enzyme without any lipid-binding domains interact with membranes to access its substrate?
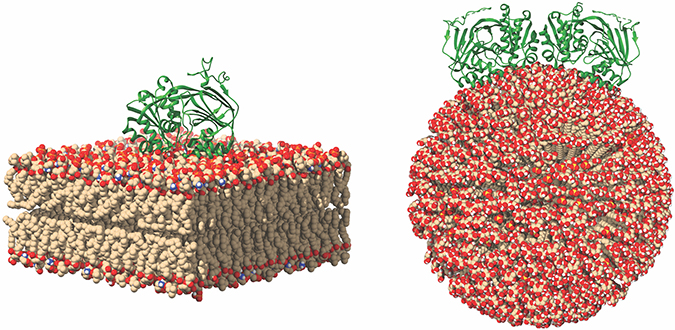 This image of SK1 binding to membranes shows potential SK1 membrane binding poses for SK1 in the presence of flat and curved membranes. Michael Pulkoski-Gross
This image of SK1 binding to membranes shows potential SK1 membrane binding poses for SK1 in the presence of flat and curved membranes. Michael Pulkoski-Gross
Previously, researchers thought SK1 translocation was dependent on other proteins. However, recent data show how SK1 can bind directly to membranes. SK1 possesses an intrinsic interface composed of two motifs: one electrostatic motif and one hydrophobic motif. Using biochemical methods, we found that these two motifs are necessary for membrane interaction, thus implicating their function as a single entity. Using hydrogen deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, we confirmed that SK1 employs a single contiguous interface that contains the two motifs. In cancer cells, disruption of this interface causes loss of membrane association and decreases SK1 activity. Past research has shown that interaction with membranes is critical for mediating SK1-dependent biologies including tumor cell invasion and endocytosis. This could provide a new avenue for targeting SK1 in diseases. Inhibition of membrane binding would deny SK1 access to its substrate, thereby inhibiting all activity.
shows an important role for SK1 in endocytic trafficking. SK1 presence at endocytic membranes would require membrane binding and curvature sensing. However, how SK1 can do this is largely unknown. Analysis of the atomic structure of SK1 revealed a potential dimerization interface. Such dimerization would align the membrane-binding interface of each SK1 monomer. This would strengthen the interaction and potentially allow for physical curvature sensing by SK1. This remains to be validated, but it’s an exciting hypothesis. Another way to potentially inhibit activity would be to inhibit dimerization, if that is required for activity and membrane binding.
Significant strides have been made in understanding the structure and function of many SL metabolizing enzymes, and exciting questions remain to be answered, especially for SK1. How can SK1 decipher the difference between the charges of different anionic phospholipids? How does the catalytic cycle progress once SK1 is at the membrane? Is dimerization required for membrane binding/curvature sensing? What role is the hydrophobic patch playing in curvature sensing?
Biophysical, biochemical and structural research will reveal the secrets of how SL enzymes work and how they might be exploited for therapeutic development.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Bacteriophage protein could make queso fresco safer
Researchers characterized the structure and function of PlyP100, a bacteriophage protein that shows promise as a food-safe antimicrobial for preventing Listeria monocytogenes growth in fresh cheeses.

Building the blueprint to block HIV
Wesley Sundquist will present his work on the HIV capsid and revolutionary drug, Lenacapavir, at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, in Maryland.

Gut microbes hijack cancer pathway in high-fat diets
Researchers at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research found that a high-fat diet increases ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut microbiome of mice, which in turn disrupts TGF-β signaling and promotes colorectal cancer.

Mapping fentanyl’s cellular footprint
Using a new imaging method, researchers at State University of New York at Buffalo traced fentanyl’s effects inside brain immune cells, revealing how the drug alters lipid droplets, pointing to new paths for addiction diagnostics.

Designing life’s building blocks with AI
Tanja Kortemme, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco, will discuss her research using computational biology to engineer proteins at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Cholesterol as a novel biomarker for Fragile X syndrome
Researchers in Quebec identified lower levels of a brain cholesterol metabolite, 24-hydroxycholesterol, in patients with fragile X syndrome, a finding that could provide a simple blood-based biomarker for understanding and managing the condition.


