JLR: Cascading errors
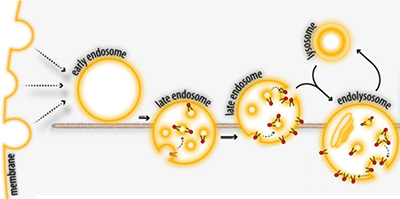 After endocytosis, membrane-spanning proteins or lipids that become part of an endosomal vesicle can face into the lumen of the late endosome and the lysosome. This makes parts of the molecule that were once on the cell surface accessible to enzymes in the lysosome.Adapted from Pribasnig et al./JBC 2015
After endocytosis, membrane-spanning proteins or lipids that become part of an endosomal vesicle can face into the lumen of the late endosome and the lysosome. This makes parts of the molecule that were once on the cell surface accessible to enzymes in the lysosome.Adapted from Pribasnig et al./JBC 2015
Lysosomal storage disorders are genetic diseases. When any one of a number of enzymes in the lysosome loses its function, the molecule it breaks down accumulates, slowly building to levels that are toxic to cells. An in the Journal of Lipid Research gives a clue as to why complex lipids known as gangliosides accumulate even in lysosomal storage disorders that don’t affect ganglioside metabolism directly. The work was led by , who discovered a lysosomal storage disorder (since named after him) in 1968.
The ganglioside GM2 is found mostly in the outer plasma membranes of cells in the nervous system. In Sandhoff disease, which is caused by mutation of the enzyme that cleaves the complex sugar in GM2’s head group, GM2 quickly accumulates in patients’ neuronal lysosomes. This accumulation can be neurologically debilitating and is often fatal.
After undergoing endocytosis as part of normal membrane turnover, GM2 becomes part of the surface of a vesicle in the lysosome (see figure). The enzyme that breaks down GM2, which resides in the lysosomal lumen, depends on binding between GM2 and an accessory protein called GM2AP to find and break down its substrate. Until now, researchers didn’t know whether GM2AP recruits the enzyme to the vesicle surface or delivers the lipid to the enzyme in solution.
Using surface plasmon resonance, scientists in Sandhoff’s lab led by postdoctoral fellow Susi Anheuser showed that GM2AP extracts gangliosides from the membrane of intraluminal vesicles. They also showed that GM2AP activity depends on the lipid makeup of those vesicles. If the vesicle has a negative surface charge, as is typical in healthy cells, GM2AP can extract gangliosides and ferry them to the relevant enzyme. If the quantity of neutral or positively charged lipids increases, the researchers observed, then that extraction is less effective, and ganglioside breakdown slows.
“GM2 degradation activity is regulated by molecules in the microenvironment of the reaction,” Sandhoff explained. “If the lipids are changed, you change everything.”
In addition to building up in some disorders as the main storage product, gangliosides can accumulate in disorders that primarily affect other lipids, such as cholesterol or mucopolysaccharides. Before now, scientists couldn’t explain why that secondary buildup occurred. This paper suggests that raising the concentration of these other lipids in the lysosomal vesicle disrupts ganglioside degradation by affecting the interaction between GM2AP and the vesicle surface.
was not involved with this JLR paper, but he studies sphingolipids at the National Institutes of Health. “Normally, simple-mindedly, you think of each enzyme carrying out a single reaction and working by itself,” he said, adding that this work complicates that view. “If one lipid is stored, and that has a negative effect on some other pathway, then the other pathways are now going to store lipids. That explains a phenomenon that’s been known for a long time.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Bacteriophage protein could make queso fresco safer
Researchers characterized the structure and function of PlyP100, a bacteriophage protein that shows promise as a food-safe antimicrobial for preventing Listeria monocytogenes growth in fresh cheeses.

Building the blueprint to block HIV
Wesley Sundquist will present his work on the HIV capsid and revolutionary drug, Lenacapavir, at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, in Maryland.

Gut microbes hijack cancer pathway in high-fat diets
Researchers at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research found that a high-fat diet increases ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut microbiome of mice, which in turn disrupts TGF-β signaling and promotes colorectal cancer.

Mapping fentanyl’s cellular footprint
Using a new imaging method, researchers at State University of New York at Buffalo traced fentanyl’s effects inside brain immune cells, revealing how the drug alters lipid droplets, pointing to new paths for addiction diagnostics.

Designing life’s building blocks with AI
Tanja Kortemme, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco, will discuss her research using computational biology to engineer proteins at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Cholesterol as a novel biomarker for Fragile X syndrome
Researchers in Quebec identified lower levels of a brain cholesterol metabolite, 24-hydroxycholesterol, in patients with fragile X syndrome, a finding that could provide a simple blood-based biomarker for understanding and managing the condition.

