JBC: New insights into the molecular weapons of the plant microbiome
Like all organisms, plants are associated with bacterial communities in which helpful and harmful bacteria compete for dominance. Among the weapons of these warring bacteria are molecular syringes that some bacteria can use to inject toxins into others. In published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, researchers at in Canada pinpointed the identity of one such toxin used by a soil-dwelling bacterium that protects plants from disease.
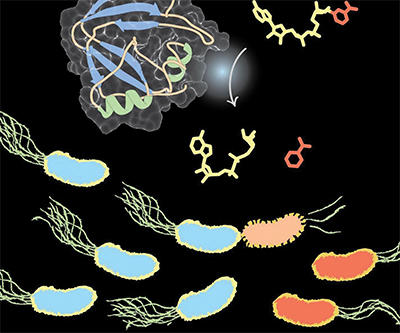 The NAD-degrading enzyme Tne2 is secreted through the type VI secretion system of the plant-protective bacterium Pseudomonas protegens.Courtesy of John Whitney/McMaster University
The NAD-degrading enzyme Tne2 is secreted through the type VI secretion system of the plant-protective bacterium Pseudomonas protegens.Courtesy of John Whitney/McMaster University
The bacterium Pseudomonas protegens can kill soil-dwelling plant pathogens, including fungi and bacteria, that attack the roots of important crops such as cotton. P. protegens releases diverse antimicrobial compounds into the soil, but was curious specifically about the compounds that it was injecting directly into other bacteria through the type VI secretion system, or T6SS.
The T6SS “is this molecular nanomachine that injects toxic protein into other species of bacteria and kills them,” Whitney said. “Plant protective bacteria that have (T6SS) can protect plants from pathogens better relative to (bacteria) that don’t have it.”
and , undergraduate students from the working with Whitney on a co-op work-study assignment, spearheaded the discovery that the toxic protein used by P. protegens against other bacteria acts on a molecule found in nearly all living cells: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+.
NAD+ is a cofactor, or “helper” molecule, in many biochemical reactions. By injecting a protein that destroys NAD+, P. protegens is able to kill other bacteria.
The team then investigated the genome sequences of hundreds of other bacteria to see how widespread the strategy of targeting NAD+ is in microbial warfare. They found that many bacteria with secretion systems carry genes similar to the one encoding the NAD-targeting toxin.
“We started to see that this isn’t just a way of killing that is enacted by plant-protective bacteria,” Whitney said. “If you look at the distribution of this (protein) among all sequenced bacteria, it appears that many different bacteria in many different environmental niches use this mode of action to outcompete other bacteria.”
The abundance of these toxins in nature raises questions: How do different bacteria in different environments evolve to resist this toxin? Are NAD-targeting toxins more effective against some bacterial species than others? Understanding the diversity of bacterial weapons is an active area of study among agricultural researchers who would like to develop better ways to fight plant diseases.
“The identification and characterization of antibacterial toxins produced by plant-protective bacteria may one day allow us to engineer these bacteria to have enhanced ability to suppress pathogens,” Whitney said.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Bacteriophage protein could make queso fresco safer
Researchers characterized the structure and function of PlyP100, a bacteriophage protein that shows promise as a food-safe antimicrobial for preventing Listeria monocytogenes growth in fresh cheeses.

Building the blueprint to block HIV
Wesley Sundquist will present his work on the HIV capsid and revolutionary drug, Lenacapavir, at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, in Maryland.

Gut microbes hijack cancer pathway in high-fat diets
Researchers at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research found that a high-fat diet increases ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut microbiome of mice, which in turn disrupts TGF-β signaling and promotes colorectal cancer.

Mapping fentanyl’s cellular footprint
Using a new imaging method, researchers at State University of New York at Buffalo traced fentanyl’s effects inside brain immune cells, revealing how the drug alters lipid droplets, pointing to new paths for addiction diagnostics.

Designing life’s building blocks with AI
Tanja Kortemme, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco, will discuss her research using computational biology to engineer proteins at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Cholesterol as a novel biomarker for Fragile X syndrome
Researchers in Quebec identified lower levels of a brain cholesterol metabolite, 24-hydroxycholesterol, in patients with fragile X syndrome, a finding that could provide a simple blood-based biomarker for understanding and managing the condition.

.jpg?lang=en-US&width=300&height=300&ext=.jpg)