JLR: Medical detectives, linked by a PubMed search
The baby looked healthy at first. But within two hours of birth, he was having severe seizures. Hospital staff at the Rambam Medical Center in Haifa, Israel, were doing a routine check when they realized that the baby was unwell. They transferred him to the neonatal intensive care unit right away and began doing tests, hoping to make a diagnosis. But every test came back negative.
The question was simple: What ails this baby?
The answer would take years to figure out. Researchers from Rambam Medical Center, Japan’s Riken Brain Science Institute and other institutions in both countries announced their solution to the medical mystery in the June issue of the Journal of Lipid Research.
A mysterious genetic ailment
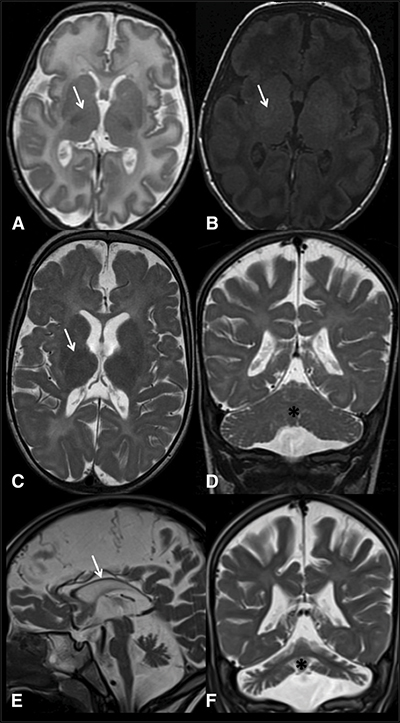 Magnetic resonance imaging scans of an Israeli child’s brain at 3 weeks (top), 1 year (middle) and 4 years of age (bottom) show limited myelin in places where it would be expected (marked with arrows). His doctors worked with a geneticist to find the genetic cause for his developmental disorder. Courtesy of Yasuhiro Horibata et al
Magnetic resonance imaging scans of an Israeli child’s brain at 3 weeks (top), 1 year (middle) and 4 years of age (bottom) show limited myelin in places where it would be expected (marked with arrows). His doctors worked with a geneticist to find the genetic cause for his developmental disorder. Courtesy of Yasuhiro Horibata et al
Hanna Mandel, a metabolic clinician, was head of the team that assessed the infant in the NICU back in 2011. Seizures in newborns usually are caused by oxygen deprivation during birth. But this baby was born by Caesarean section, and his skin color and breathing had looked perfectly healthy. More than a dozen routine tests came back normal. The child had no infection, no problem with known metabolites, no clues in his urine or cerebrospinal fluid. After a battery of routine tests and an extra metabolic workup, Mandel said, they found nothing that could explain the child’s illness.
So the doctors sent the child, by this time three weeks old, for brain scans. The images showed a lack of myelin, the essential fatty coating around nerves. Myelin works like the plastic insulation around an electrical wire. If the insulation isn’t there, the wires — in this case, neurons — cannot carry an electrical signal as far or as fast. This deficiency may have affected the boy’s development.
As he grew older, the child’s development lagged; he never began to move on his own. Follow-up scans showed that his myelin still was not developing and other parts of his brain were beginning to atrophy.
When the child was 4 years old, , a specialist in rare genetic diseases at Hadassah–Hebrew University Medical Center in Jerusalem, led a team that sequenced and analyzed much of the boy’s genome, looking for homozygous mutations that he might have inherited from both of his parents, who are cousins.
Elpeleg found 13 sites in the boy’s genome where he had inherited rare coding variants from both parents. By looking at his healthy family members’ genes, the team could rule out many of these sites as causing the child’s problems. The mutation the researchers found responsible was a single-nucleotide change in a gene called ethanolamine phosphotransferase 1, or EPT1. The mRNA of the gene was much shorter in the boy than in a healthy control. At the time, no one ever had diagnosed a patient with an EPT1 mutation.
When the geneticist found the mutation, Mandel went straight to PubMed, a database housing medical and biological research. She was looking, she said, “for someone who would be interested to study the pathogenicity of the EPT1 mutation.”
She found the world experts on the gene in question.
Bringing together an international team
Several years earlier, Yasuhiro Horibata had been a graduate student in the laboratory of , who studies lipid physiology at the prestigious RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan.
The two had discovered that the EPT1 gene codes for an enzyme that puts the finishing touches on the lipid phosphatidylethanolamine, or PE for short. PE makes up about a fifth of all the phospholipids in the brain. They published their findings in in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Mandel found that paper and wrote to Hirabayashi. Soon she, Hirabayashi and Horibata, who was by then a professor at Dokkyo University, hatched a collaboration by email, and the Israeli team shipped a sample of the child’s tissue to Japan.
The Japanese team measured enzyme activity and confirmed that it was very low compared with a healthy control, because the incorrectly shortened protein was destroyed immediately by the cell’s quality-control systems. They looked for changes in the child’s skin cells, measuring all the lipids the cells produced. The lack of EPT1 only slightly reduced the amount of PE in his tissue. This was unexpected, since PE was the main known product of EPT1 activity.
However, the shortage of EPT1 dramatically reduced the amount of another molecule, plasmalogen, a lipid product made from PE and enriched in myelin. It seemed that the cells were using other enzymes to compensate for PE production but not enough to rescue the plasmalogen synthesis. The researchers concluded that even though its PE-manufacturing work is duplicated by another enzyme, EPT1 is important for making myelin in the normal brain. That work is described in the team’s new JLR paper.
Hope for the future
The researchers solved the genetic piece of the boy’s puzzling disease. Last year a British team reported on a patient with similar symptoms and a similar mutation, making the Israeli boy only the second in the medical literature with an EPT1 disorder.
However, as for many people living with rare genetic diseases, his treatment options are limited. He is paraplegic and unable to see or hear. His seizures have worsened.
Mandel emphasizes the positive aspects of the child’s life. “He lives in a beautiful Arab village in Northern Israel, in a beautiful house with his parents and sister,” she said. “During the day, he is going to a rehabilitation center near his home village, where he gets all the paramedical support one could think of.”
Meanwhile, the doctors have offered his parents genetic counseling based on their research. “The couple is aiming for preimplantation genetic diagnosis for future pregnancies,” Mandel said. The procedure, which involves screening embryos made by in vitro fertilization for specific genetic diseases before implanting them, could help ensure that any future children the couple may have escape the effects of EPT1 deficiency.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Bacteriophage protein could make queso fresco safer
Researchers characterized the structure and function of PlyP100, a bacteriophage protein that shows promise as a food-safe antimicrobial for preventing Listeria monocytogenes growth in fresh cheeses.

Building the blueprint to block HIV
Wesley Sundquist will present his work on the HIV capsid and revolutionary drug, Lenacapavir, at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, in Maryland.

Gut microbes hijack cancer pathway in high-fat diets
Researchers at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research found that a high-fat diet increases ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut microbiome of mice, which in turn disrupts TGF-β signaling and promotes colorectal cancer.

Mapping fentanyl’s cellular footprint
Using a new imaging method, researchers at State University of New York at Buffalo traced fentanyl’s effects inside brain immune cells, revealing how the drug alters lipid droplets, pointing to new paths for addiction diagnostics.

Designing life’s building blocks with AI
Tanja Kortemme, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco, will discuss her research using computational biology to engineer proteins at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Cholesterol as a novel biomarker for Fragile X syndrome
Researchers in Quebec identified lower levels of a brain cholesterol metabolite, 24-hydroxycholesterol, in patients with fragile X syndrome, a finding that could provide a simple blood-based biomarker for understanding and managing the condition.

